Developer Experience with Spring Cloud
Spencer Gibb, Dave Syer, 2015Authors
Spencer Gibb,
@spencerbgibb,
sgibb@pivotal.io
Dave Syer,
@david_syer,
dsyer@pivotal.io
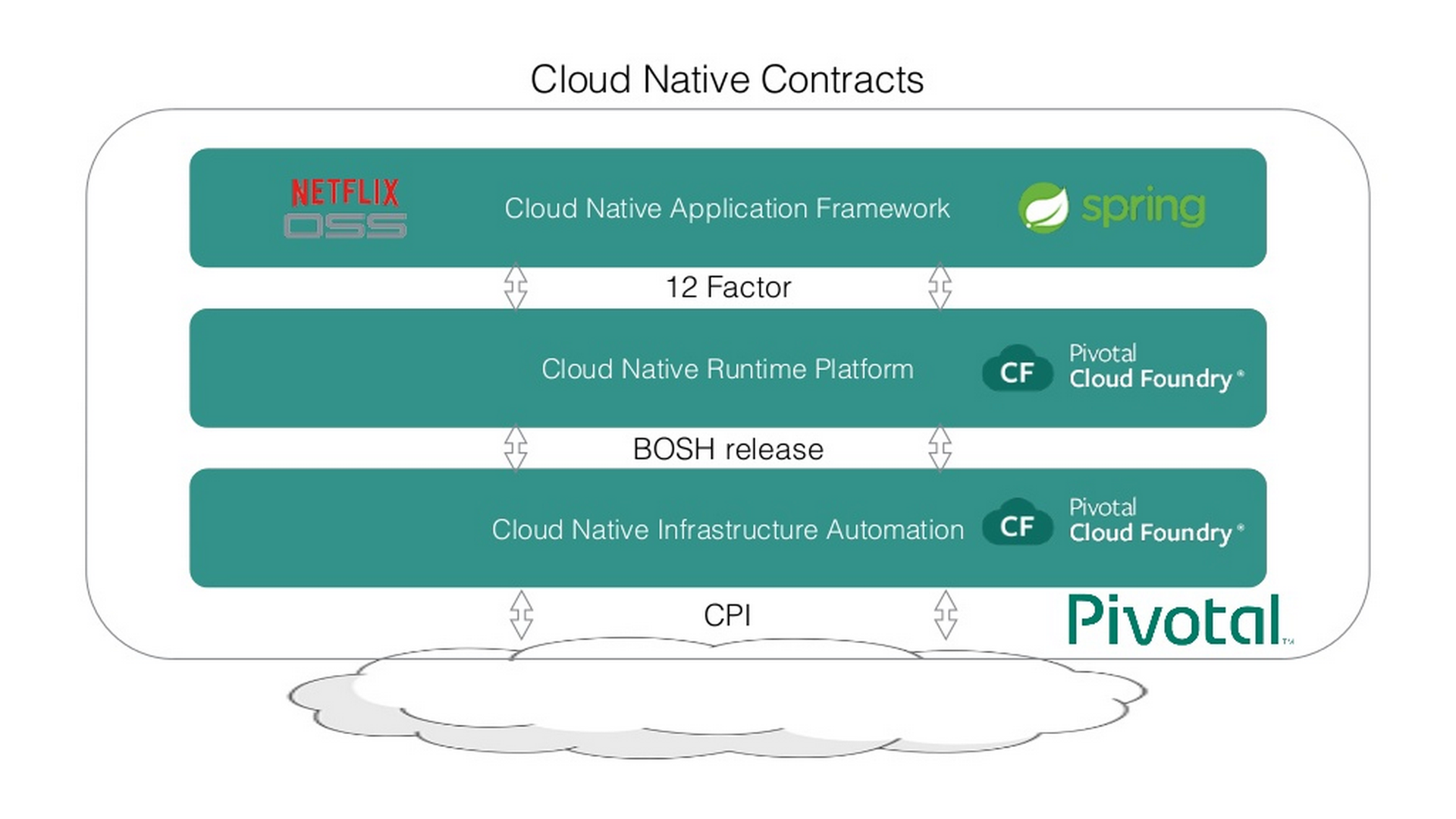
Cloud Native Contracts

With thanks to @littleidea
Developer Experience
- Microservices lead to a very open flexible architecture
- Developer needs to work on isolated codebase
- No-one wants to re-deploy the universe for every commit
- What tools and techniques are available to help?
- How can Spring, Spring Cloud, Cloud Foundry play a role?
Devops open data
- "if you build it you run it" (or at least "own it")
- 12-factor principles, Spring Boot and Spring Cloud Environment support
- logs (sensible defaults, stdout)
- actuator endpoints: /trace, /routes, /mappings, /env, /configprops, /beans, /autoconfig
Debugging and fault finding
Your app won’t always work first time. How to diagnose the problem?
- collecting logs from remote system (/logs endpoint and
cf logs) - changing log levels at runtime
- other useful actuator endpoints: /env, /trace, /mappings, /autoconfig
- feature switches
- remote debugger (see later: Spring Boot Devtools)
- deploy locally
Service discovery background
Spring Cloud Discovery
spring-cloud-commons: useful abstractionsDiscoveryClient,LoadBalancer,@EnableServiceDiscoveryspring-cloud-netflix: Eureka and Ribbonspring-cloud-consul: Hashicorp Consulspring-cloud-zookeeper: Zookeeperspring-cloud-cloudfoundry: cloud controller APIspring-cloud-lattice: receptor (diego controller) API
Cloud Foundry native discovery
- Uses the Cloud Controller API
- Discovery only, no registration
- Requests are made through gorouter
Lattice native discovery
- Uses the Receptor API from Diego
- Discovery only, no registration
- Adds 'cloud' and 'lattice' profiles
Connectors (using service name)
- Mysql, Redis & Rabbitmq
Eureka on Lattice & Cloud Foundry
- Eureka can run on Lattice and CF
- Provides discovery and registration
- Can be managed on Pivotal Cloud Foundry (Commercial)
Routing from remote system to IDE
- local dev experience
- use proxy to tunnel back to IDE (e.g. ngrok)
- demo with Boot Dashboard
Loadbalancer configuration models
- flag to enable local route
- prefer route that “looks local”
- flag a request (e.g. header with correlation ID)
Customizing Ribbon
- Ribbon is a client side smart load-balancer from Netflix OSS
IRule: Load-balancing algorithm (round-robin, random, etc…)ServerList: Where to get the list of servers to load-balance.ConfigurationBasedServerList:ribbon.<clientname>.listOfServersproperty
DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList: via eurekaConsulServerList: via hashicorp consulZookeeperServerList: …
ServerListFilter: filters list of servers.
Ribbon Annotations
@RibbonClients- Optionally defines default java config classes for all ribbon clients.
- Allows multiple
@RibbonClientannotations.
@RibbonClient: allows configuration for a named ribbon client.
Ribbon in Integration Tests
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@SpringApplicationConfiguration(classes = MyTests.Application.class)
@WebIntegrationTest(randomPort = true)
public class MyTests { /*...*/
@Configuration
@RibbonClient(name = "localapp",
configuration = LocalRibbonClientConfig.class)
protected static class Application { /*...*/ }
@Configuration
static class LocalRibbonClientConfig {
@Value("${local.server.port}")
private int port = 0;
@Bean
public ServerList<Server> ribbonServerList() {
return new StaticServerList<>(new Server("localhost", this.port));
}
}
}Stubbing
High level:
- Greenfield (dependent services don’t exist yet, write stubs)
- Brownfield (dependent services exist and have published stubs)
Example tools/approaches:
- publish producer stubs vs. consumer tests
- "forced stubbing": micro-infra from 4finance
- ad-hoc stubbing: accurest, wiremock, stubby4j, Spring MVC
- embedded stubs vs. remote stubs
Stubbing Brownfield Services
Create Wiremock stubs using tests or dsl
- AccuREST uses a groovy dsl to create integration tests and stubs.
- Spring REST Docs uses tests to generate snippets for documentation and can be used to create stubs.
- Run Wiremock using generated stubs
- Run consuming services against Wiremock stubs
Stubbing: AccuREST DSL
Generates a MockMVC test and a Wiremock stub
import io.codearte.accurest.dsl.GroovyDsl
GroovyDsl groovyDsl = GroovyDsl.make {
request {
method 'GET'
url '/foo'
}
response {
status 200
headers {
header 'Content-Type' : 'application/json;charset=UTF-8'
}
body '''{ "value" : 42 }'''
}
}Stubbing: Spring REST Docs
@Before
public void setup() {
this.mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(this.context)
.apply(documentationConfiguration()
.snippets().withDefaults(curlRequest(),
httpRequest(),
httpResponse(),
new WiremockStubSnippet()))
.build();
}
@Test
public void foo() {
this.mockMvc.perform(get("/foo")
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andDo(document("foo"));
}Stubbing: Wiremock Stub
{
"request": {
"method": "GET",
"url": "/foo"
},
"response": {
"status": 200,
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json;charset=UTF-8"
},
"body": "{\"value\":42}"
}
}Greenfield Stubbing: Spring MVC
@Controller
public class StubFleetLocationServiceApplication {
@RequestMapping("/locations")
public String home() {
return "forward:/stubs/locations.json";
}
...
}Nice side effect: mock MVC and restdocs for tests and docs can be used to verify real service contract
Stubbing: 4finance stubrunner
- Publish stub files to nexus repository (or local maven repo)
- Describe all services dependencies in
application.yml Stubrunner uses list of dependencies
- Grabs stubs from repository
- Runs a wiremock server for each dependency using fetched stubs
- Registers server in service discovery
- Consuming service can function against stubs (DEMO)
Hot reloading and code swapping
- Basic IDE features (JVM hotswap and resource reload)
- Spring Boot devtools - app restart and browser plugin
- STS
- Spring Loaded (Grails, JHipster)
- JRebel
Hot reloading locally
App monitors its classpath and restarts when changes detected:
Hot reloading with browser
Browser plugin automatically refreshes views:
Hot reloading and debugging
Hot reloading of “local” application code deployed on Cloud Foundry / Lattice
- Spring Boot support via devtools
- classloader flushes dirty resources
- remote debug also possible (but slow)
ALM
How does new code enter a build pipeline and get promoted to production?
- adhoc deployment and mixed local-remote is great for dev time
- always automated downstream
- always part of CI process
- stay close to production platform (e.g. use Cloud Foundry for everything)
- don’t redeploy the universe for every change
Debugging requests
- live vs. historic
- /trace endpoint
- distributed tracing (http and messages)
- cf/lattice logs (http and messages)
- https://ngrok.com (http)
Database/middleware: Docker
- standard docker images exist for all common middleware
- perfect for development
- can be used in production with care
Middleware: Discovery and DI
How to wire up your application code to required middleware, and make the same code run in all environments?
- use autoconfiguration
- use Spring Cloud Connectors (a bit)
- use Spring Cloud Stream for messaging
Provisioning a system for testing
- Docker compose (great for repeatability)
- Locally with VirtualBox
- Remotely: Lattice AWS, PCF, etc.
- CI systems native support (travis, bamboo, etc.)
Links
/